Understanding Why an Erection Won’t Be as Hard – The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy
Androhaus – shockwave therapy
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is one of the most common conditions affecting men over the age of 30. It can manifest as difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, or when an erection won’t be as hard as it used to be. Although it can cause emotional distress, the condition is primarily a physiological issue related to blood flow, vascular health, and nerve response.
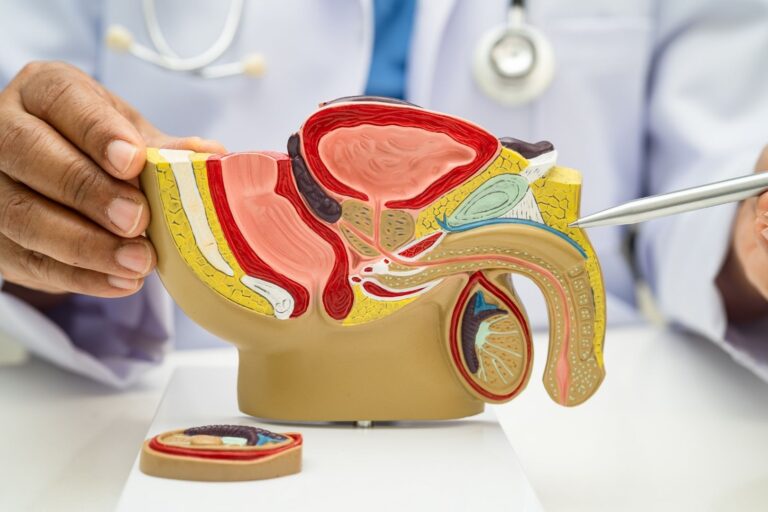
The Physiology of an Erection
A normal erection depends on complex coordination between the nervous system, hormones, blood vessels, and smooth muscle tissue.
When sexually stimulated, the brain releases nitric oxide, which relaxes the smooth muscle within the penile arteries. This allows blood to flow into the corpora cavernosa – the two sponge-like structures that expand and harden the penis. If this process is interrupted at any stage, the erection may not reach full rigidity or may subside prematurely.
Why an Erection Might Not Be as Hard
Several biological and lifestyle factors can lead to a reduction in erection hardness:
- Vascular disease: Narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis) reduces penile blood flow.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage both nerves and small arteries.
- Low testosterone: Hormonal imbalance can lower libido and affect erectile quality.
- Medication: Certain blood pressure and antidepressant drugs can reduce erectile response.
- Psychological stress: Chronic anxiety, depression, or performance pressure can interfere with arousal.
- Lifestyle: Smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and lack of exercise all reduce vascular performance.
Understanding which mechanism is affected is key to selecting the most effective treatment.
The Role of Shockwave Therapy in Erectile Function
Low-intensity extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (Li-ESWT) is an emerging, evidence-based treatment for men experiencing erectile
dysfunction.
Rather than relying on medication, this therapy stimulates natural healing within the penile tissue.
Mechanism of Action
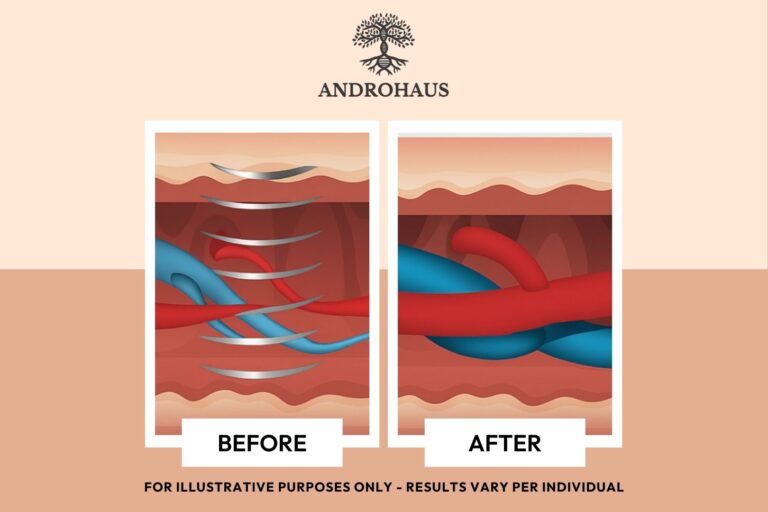
Shockwave Therapy delivers focused acoustic energy waves to the erectile tissue. These waves trigger a biological response known as neovascularisation — the formation of new blood vessels.
This process improves circulation, oxygen delivery, and endothelial function, all of which are critical for maintaining a firm erection.
Scientific studies have shown that this stimulation increases the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and nitric oxide synthase, improving both blood flow and nerve sensitivity.
Clinical Evidence
A growing body of clinical research supports Shockwave Therapy as a promising approach for men with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction.
Key findings from recent studies:
- Improved Erection Hardness Scores (EHS): Many patients report measurable improvement after six sessions.
- Sustained results: Benefits can last several months to years, especially with healthy lifestyle changes.
- No adverse side effects: Unlike oral medication, shockwave treatment is drug-free and non-invasive.
It is important to note that not all men respond equally; individuals with severe vascular damage or advanced diabetes may require combined or alternative therapies.
Who Can Benefit
Shockwave Therapy is most effective for men whose erection won’t be as hard due to reduced penile blood flow rather than neurological or psychological causes.
It can be used as:
- A first-line treatment for mild ED
- An adjunct to medication or hormone therapy
- A maintenance therapy for men recovering from prostate surgery or long-term ED
Every case should begin with a medical assessment, including hormonal profiling and vascular evaluation.
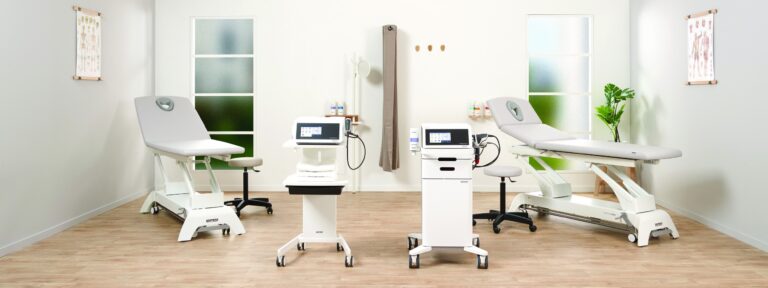
Safety and Procedure Overview
The treatment is performed in a clinical setting using a handheld device that emits targeted sound waves.
Each session typically lasts 15–20 minutes and requires no anaesthesia or recovery time.
Men may experience mild tingling during the procedure, but the therapy is generally painless. After completing the full course (usually 6–8 sessions),
most patients experience a noticeable improvement in rigidity and spontaneous erections.
Lifestyle and Preventive Considerations
Shockwave Therapy provides a physiological foundation for recovery, but its effectiveness increases when combined with lifestyle optimisation:
- Regular cardiovascular exercise
- Balanced diet rich in antioxidants
- Adequate sleep and stress management
- Smoking cessation
- Regular medical check-ups for blood pressure, lipids, and glucose levels
Addressing these factors supports both erectile health and general wellbeing.
When an erection won’t be as hard as before, it is often a signal of reduced vascular function rather than a purely psychological problem.
Modern medical advances, such as Shockwave Therapy, allow targeted restoration of blood flow and tissue vitality without medication or surgery.
With proper assessment and personalised treatment, most men can regain normal erectile function safely and effectively.
References
- Vardi Y, et al. Low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy for erectile dysfunction: a short-term prospective pilot study. J Urol. 2010.
- Gruenwald I, et al. Shockwave therapy for ED: clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. Int J Impot Res. 2013.
- Dong L, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-intensity shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urology. 2019.
- European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines, 2024.